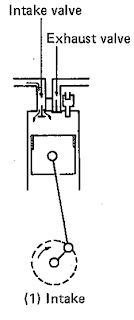
A 4-cycle engine completes the four stroke of intake, compression, expansion, and exhaust against 2 reciprocating motions of the piston, or while the crankshaft makes 2 rotations.
Followings are the descriptions based upon a diesel engine.
1. Intake Stroke
2. Compression Stroke
The intake valve is closed when the piston lowering on its intake stroke passes through the bottom dead center (BDC). The piston, then, again starts upward motion so that the air sealed in the cylinder is compressed. The compression pressure is approximately 30 to 40 kg and the temperature rises to about 400 to 500⁰C.
 The ratio of the cylinder volume (V) at the time when the piston is reached to the lowest position, or the bottom dead center (BDC), and the cylinder volume (V') at the time when the piston is raised to the uppermost position, or the top dead center (TDC) is called the compression ratio. The compression ratio of a diesel engine is about 14 to 22, while that of a gasoline engine is about 5 to 10.
The ratio of the cylinder volume (V) at the time when the piston is reached to the lowest position, or the bottom dead center (BDC), and the cylinder volume (V') at the time when the piston is raised to the uppermost position, or the top dead center (TDC) is called the compression ratio. The compression ratio of a diesel engine is about 14 to 22, while that of a gasoline engine is about 5 to 10.
3. Expansion Stroke
When fuel is injected from the injection nozzle at the end of the compression stroke, or just before the piston reaches the top dead center (TDC), the fuel is mixed the air heated to a high temperature by the compression so that the fuel is burnt in an extremely short time. At that instant, the combustion pressure in the cylinder is raised to 80 to 110kg/cm2 and pushes down the piston which just passed the top dead center so that the crankshaft is rotated through the connection rod.
There are following methods for injecting the fuel at this instant. The one is the method by which the fuel is injected from the injector directly into the combustion chamber called the direct injection type, the other is the method by which the fuel is previously injected into the pre-combustion chamber for the purpose of perfectly mixing with the air and then injected into the main combustion chamber called the pre-combustion chamber type or the swirling chamber type.
In case of a gasoline engine, at the end of the compression stroke when the piston reaches the top dead center (TDC), electric spark made by the ignition plug ignite the mixed gas.
At that instant, the expansion pressure of gas is approximately 30 to 40kg/cm2.
4. Exhaust Stroke
The exhaust valve opens just before the piston reaches the bottom dead center (BDC) and the combustion gas is forced out of the cylinder rising motion by upward movement of the piston.
One cycle is completed by the above mentioned motion, and the cycle is repeated from the intake stroke again so that the engine continues its operation.




0 Responses to "Operating Principle of 4-Cycle Engine"
Posting Komentar